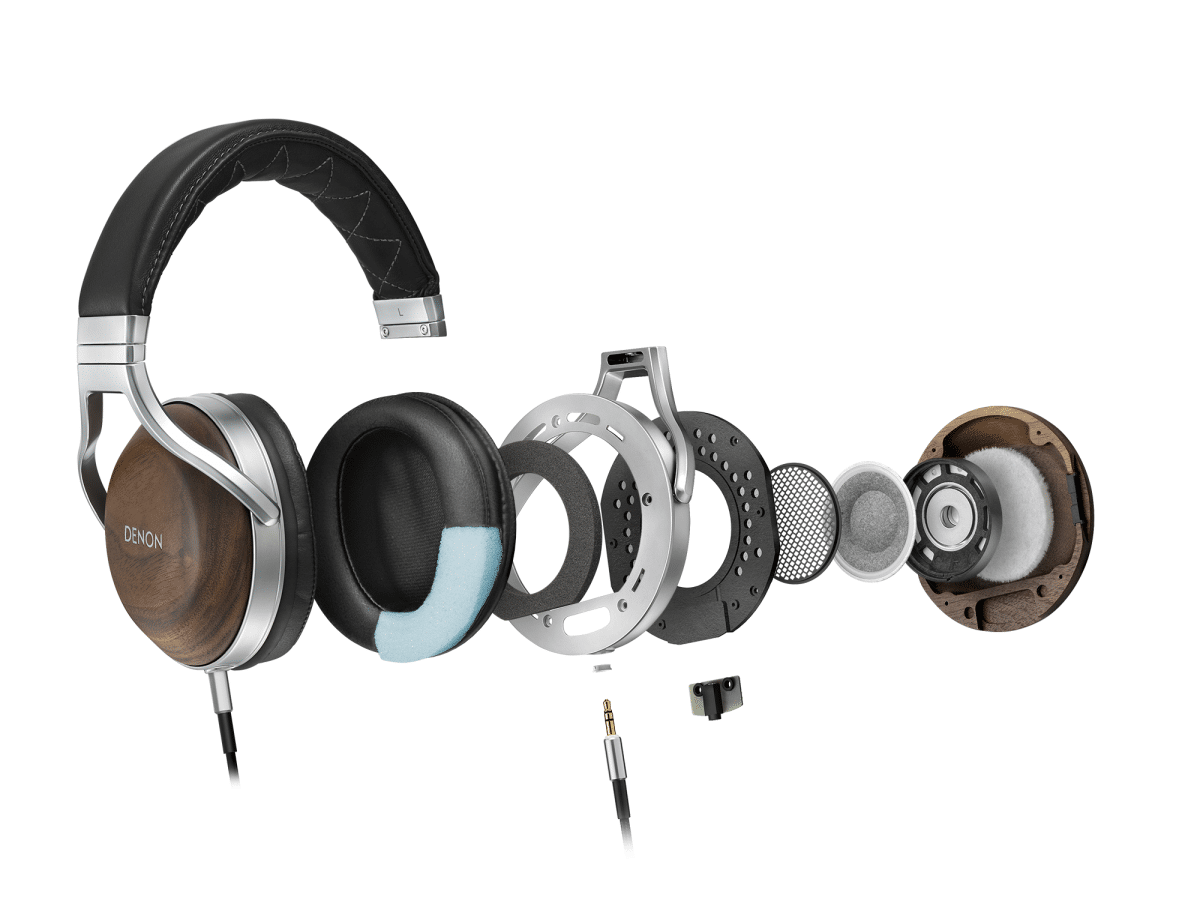

What Are Headphone Drivers?
Headphone drivers are the most crucial part of any headphone and are responsible for converting an electrical signal into sound. They are an electromagnetic transducer that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy, converted into acoustic energy. In other words, they transform the electrical signal into sound.
The drivers within your headphones can range in size from as small as a grain of sand to as large as a dinner plate. The most common size is 40mm.
Headphone Driver Size
Size is an essential factor in headphones, and the driver’s size is a big part of this. The driver’s size directly correlates to how much bass you will get and how much detail you will be able to hear. For example, the larger the driver, the more bass you will get. This is because the speaker’s cone is larger and can move further, creating more air pressure and producing more bass.
On the other hand, a smaller driver will produce more detail as it can move faster. This is because a smaller driver has a shorter wavelength and can move more quickly than a larger driver.
However, this does not mean that a large driver cannot produce detail or that a small driver cannot produce bass. It all depends on the design of the driver.
Headphone Driver Materials
There are many different types of materials that can be used to produce a driver. Each different material has its unique properties which will affect the sound quality that the driver produces.
The two most common materials used to produce a driver are:
- ✓ Paper/Cotton
- ✓ Kevlar/Fiberglass/Aramid
The paper/cotton drivers are typically found in more budget-friendly headphones and will not produce excellent sound quality. They are also known as moving coil drivers and are the most commonly used type of driver.
The second type of driver is the Kevlar/Fiberglass/Aramid drivers. These are typically found in higher-end headphones as they produce better sound quality. They are also known as planar magnetic drivers and electrostatic drivers.
Are more drivers better?
There are many headphones out there that have multiple drivers in them. For example, the Sennheiser HD800 has two separate drivers in each earpiece.
The idea behind these headphones is that they will produce a wider soundstage, more detail and more bass. However, this is not always the case. Many people find that these headphones sound worse than their single driver counterparts because they cannot produce a coherent sound.
The only time that multiple drivers improve the sound quality is when they are working together as a single unit. For example, in a pair of speakers, having numerous drivers will improve the sound quality because they work together to produce the overall sound. However, in headphones, having multiple drivers does not have the same effect. This is because they are designed to be used in one ear only, and so you cannot hear the sound coming from both drivers at the same time.
Types of Headphone Drivers
There are many types of headphone drivers; we are going to look at seven types of headphones drivers:
- ✓ Dynamic / Moving Coil
- ✓ Planar Magnetic
- ✓ Electrostatic
- ✓ Ribbon
- ✓ Piezoelectric
- ✓ Balanced Armature
- ✓ Bone Conduction
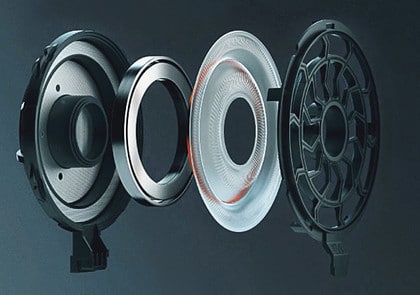
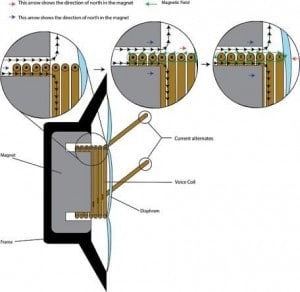
Dynamic / Moving Coil
The Dynamic Headphone Driver is the most common type of headphone drivers and is found in most headphones. They are typically found in budget-friendly headphones and are known as moving coil drivers.
They work by having a magnet attached to a coil of wire. When an electrical current is passed through the wire, it creates a magnetic field. This magnetic field then interacts with the magnet, causing it to move. This movement then causes the diaphragm to move, and this movement is then converted into sound.
The main parts of a dynamic driver are:
- ✓ Magnet
- ✓ Voice Coil
- ✓ Diaphragm
The magnet magnetizes the voice coil, which causes it to move. This movement causes the diaphragm to move, which then produces sound.
Many different types of magnets can be used in a dynamic driver. The most common ones are:
Alnico magnets are typically found in budget-friendly headphones and are known for their warm sound. Ceramic magnets are more robust than Alnico magnets and so can produce more bass. Neodymium magnets are the strongest of the three and so are also capable of making the most bass.
Depending on the magnet within your driver, your headphones will produce different amounts of bass. However, to create a natural bass response, headphones need to have a good seal around your ear. This is because bass frequencies are the ones that are most affected by the seal. The dynamic driver is capable of producing bass frequencies that range from 20Hz to 20,000Hz.
A common complaint that people have with dynamic driver headphones is that they are not very detailed. This is because the movement of the driver is not very fast. However, they do have a wide frequency response and can produce a wide range of frequencies. Non-linear distortion is quite common with dynamic drivers, and so they are not as accurate as other types of drivers, causing audio distortion as the volume is increased.
Planar Magnetic (Orthodynamic Drivers)
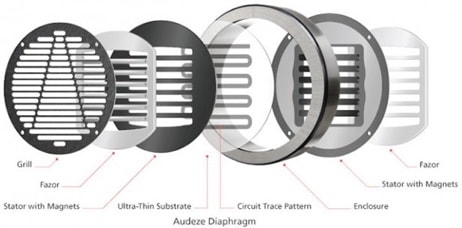
A planar magnetic driver is a type of dynamic driver. It works similarly to a traditional dynamic driver, but instead of having a coil of wire attached to the magnet, it has a flat diaphragm that moves.
Planar magnetic drivers are typically found in higher-end headphones and are known for their very accurate sound. They are also known as orthodynamic drivers. Planar magnetic drivers’ main benefit is that they require less energy to produce a given amount of sound than traditional dynamic drivers.
The main parts of a planar magnetic driver are:
- ✓ Magnet
- ✓ Voice Coil
- ✓ Diaphragm
The main difference between a planar magnetic driver and a traditional dynamic driver is that the diaphragm is much thinner and can move more quickly. This means that it is capable of producing more detail than a conventional dynamic driver.
The magnets used in planar magnetic drivers are typically made of Neodymium, but can also be made of Alnico or Ceramic. The type of magnet used will affect the amount of bass produced by the driver.
Planar magnetic drivers are capable of producing frequencies from 20Hz to 100,000Hz. They are also very linear and so do not produce any distortion at higher volumes. They also have a very wide frequency response and are capable of producing a wide range of frequencies.
Electrostatic
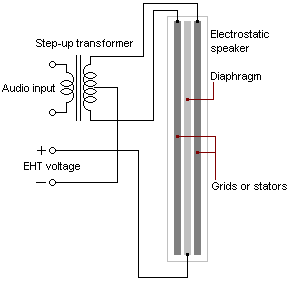
An electrostatic driver uses electrostatic forces to move the diaphragm. It is the most accurate type of driver and so is typically found in high-end headphones. They are also known as a planar driver or an electrostatic transducer.
The main parts of an electrostatic driver are:
- ✓ Grid
- ✓ Condenser
- ✓ Diaphragm
The diaphragm is charged with a static charge that causes it to move. The grid and the condenser work together to create the electrostatic field. The grid is charged negatively and attracts the positively charged diaphragm.
Electrostatic drivers are capable of producing frequencies that range from 20Hz to 100,000Hz. They are also very linear and so do not produce any distortion at higher volumes. They also have a very wide frequency response and are capable of producing a wide range of frequencies.
Electrostatic drivers offer superior soundstage to any other driver, but they are also the most expensive out of all the different headphone drivers. They are typically found in high-end headphones and so are not suitable for portable headphones.
Ribbon

A ribbon driver is a type of dynamic driver made from a thin strip of metal or plastic. They are known for their smooth, natural sound and are typically found in high-end headphones.
The main parts of a ribbon driver are:
- ✓ Magnet
- ✓ Voice Coil
- ✓ Diaphragm
The diaphragm is made from a thin piece of metal or plastic that is suspended between two magnets. The voice coil is attached to the diaphragm, and when an electrical current is passed through it, it creates a magnetic field. This magnetic field interacts with the magnets’ magnetic field, causing the diaphragm to move.
Ribbon drivers are capable of producing frequencies that range from 20Hz to 80,000Hz. They are also very linear and so do not produce any distortion at higher volumes. They also have a very wide frequency response and are capable of producing a wide range of frequencies.
Ribbon drivers are typically found in headphones designed for professional use, such as studio headphones and mixing headphones. However, they are also found in some high-end consumer headphones.
Piezoelectric

A piezoelectric driver is a type of dynamic driver that uses piezoelectricity to move the diaphragm. It is typically found in high-end headphones and is known for its clear sound. It is also known as a crystal driver or a quartz driver.
The main parts of a piezoelectric driver are:
- ✓ Diaphragm
- ✓ Back Plate
- ✓ Piezoelectric Film
The diaphragm is made from a thin layer of quartz crystal and can move when an electric current is passed through it. The backplate is made from a material that can withstand the high voltages required to produce sound. It is then attached to the diaphragm using a flexible adhesive; the piezoelectric film is then placed between the backplate and the adhesive. This film is then charged with an electric current which causes it to expand and contract. These movements cause the diaphragm to move, which then produces sound.
A piezoelectric driver is capable of producing frequencies that range from 20Hz to 20,000Hz. They are also very linear and so do not produce any distortion at higher volumes. They also have a very wide frequency response and are capable of producing a wide range of frequencies.
The main disadvantage of a piezoelectric driver is that they require a lot of power to produce sound. This means that they are typically found in high-end headphones as they have a good amplifier built within them. Another disadvantage is that they are not very efficient and so do not produce much sound for the amount of power that they use. They are also not very durable and can be easily damaged if they are dropped or knocked around too much. However, this does mean that they do not require much maintenance and will last for a long time if you take good care of them.
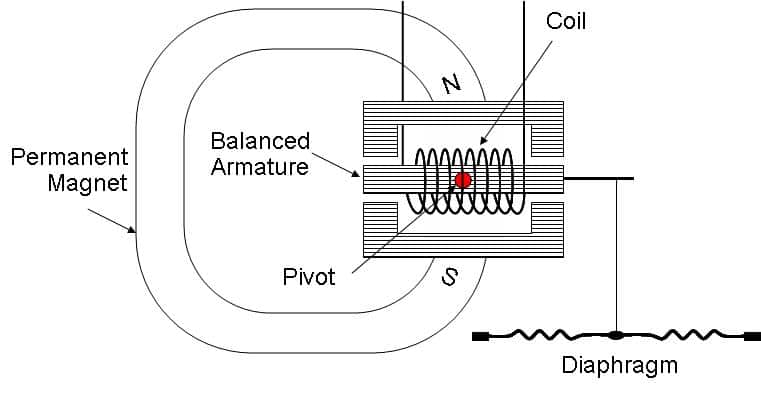
Balanced Armature
A balanced armature driver uses a single piece of wire for both the driver’s positive and negative sides, which allows it to move more freely than other types of drivers. It has been designed in such a way as to reduce non-linear distortion and so produces very accurate sound quality. It is also known as an armature driver or an air motion transformer driver. They are typically found in higher-end headphones and so are not suitable for portable headphones. They can be found in both open-back and closed-back headphones.
The main parts of a balanced armature driver are:
- ✓ Voice Coil
- ✓ Magnet
- ✓ Diaphragm
The voice coil is a single piece of wire used for both the driver’s positive and negative sides. This allows it to move more freely than other drivers. The magnet is attached to one end of the voice coil, and the diaphragm is attached to the other end. The movement of the voice coil causes the diaphragm to move, which then produces sound. The movement of the diaphragm can be controlled by changing the current through the voice coil.
Balanced armature drivers are capable of producing frequencies that range from 20Hz to 20,000Hz. They are also very linear and so do not produce any distortion at higher volumes. They also have a very wide frequency response and are capable of producing a wide range of frequencies. They can produce very detailed sound, making them ideal for listening to instruments such as guitars. They also have a vast soundstage, making them suitable for gaming headsets. However, they do not produce as much bass as other headphone drivers, so they are not ideal for listening to music with lots of bass or EDM tracks.
Bone Conduction
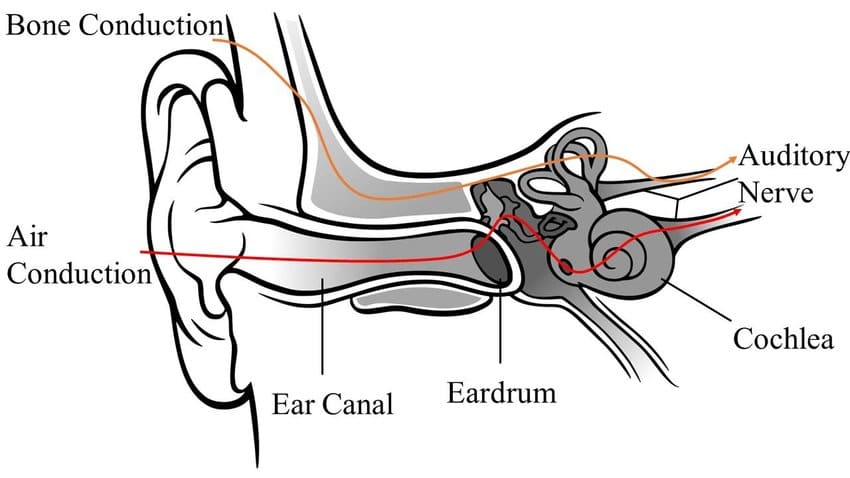
These headphones use bone conduction to transmit sound directly into your inner ear through your bones, bypassing your eardrum completely. This means that they can transmit sound even when there is no air pressure being created, such as when you are underwater or in a vacuum. They are typically found in fitness trackers and hearing aids, and so they are not suitable for listening to music on the go.
They work by having a transducer that creates vibrations in your skull, transmitting sound waves directly into your inner ear via your skull bones. This means that they do not require an air seal around your ear canal and can be used whilst swimming.
Bone conduction headphones can produce frequencies that range from 20Hz to 20,000Hz, but they do not produce as much bass as other types of headphones because there is no air pressure being created within your ear canal. This means that they are only really suitable for listening to speech or podcasts whilst on the go or swimming. They are also only really ideal for one ear at a time as you can only hear one frequency at a time through each ear due to bone conduction limitations.
The main parts of a bone conduction driver are:
- ✓ Transducer
- ✓ Magnet
- ✓ Diaphragm
The transducer creates vibrations in your skull, transmitting sound waves directly into your inner ear via your skull bones. The magnet is not used to create vibrations in the transducer. The diaphragm is not used to create vibrations in the transducer.
Bone conduction drivers are typically found in sports headphones. They are also used in some Bluetooth headsets, like the AfterShokz Trekz Titanium. However, many people find that bone conduction drivers do not work well for listening to music on the go as they cannot produce as much bass as other types of drivers.
